RESEARCH 》 Power consumption of my Home Lab devices for research
| AMD RYZEN 3 1200 - FreeNAS Storage array build | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| My Intel Core i7-5820K - Desktop build | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| My Intel Celeron CPU 1037U Mini PC WAN Optimization Device | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| My HP Envy 15-J111TX Laptop | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| My Dell 15R 5537 Laptop | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| My Acer Aspire 4810T Laptop | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
* No Battery, so no charging.
|
| Raspberry Pi2 Device | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| NETGEAR RN104 ReadyNAS | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| APC BX600C-IN UPS - APC Back-UPS 600 | (UPS not powered-on but connected to live power socket) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| APC BX600CI-IN UPS - APC Back-UPS 600 | (UPS not powered-on but connected to live power socket) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| BenQ LED Monitor 24'' GW2470HM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| LG LCD TV Monitor 23'' M237WA-PT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Samsung LCD Monitor 22'' 2243NWX | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

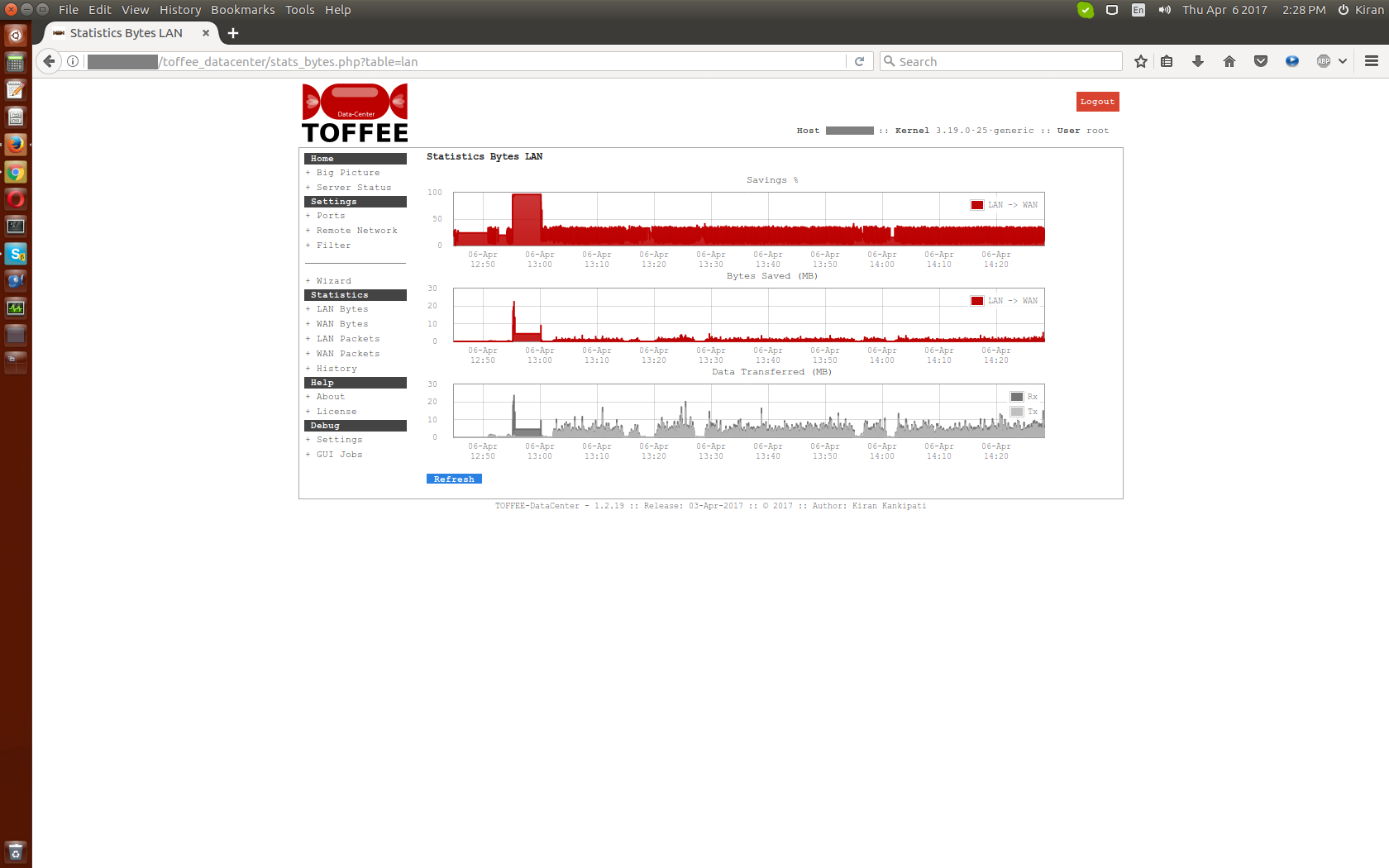
Here is my power-consumption measurements of various devices deployed within my home lab. I measured via my kill-a-watt sort of power-meter which is fairly reliable and accurate. I checked its accuracy with various standard load such as Philips LED laps and other constant power-consuming devices to make sure that the power-meter is precise.
So far I maintained this data in my personal Google drive spreadsheet documents. But now I thought perhaps its good to share these numbers so that it is useful for various users to access their equipment such as:
- decide UPS and battery backup ratings
- off-grid solar power installations
- choose new upgraded hardware which consumes less power and deliver better performance such as SSD over traditional HDD, new CPU, new Monitor, new laptop, servers, desktops and so on. And discard obsolete old hardware.
- choosing the right PSU (power supply unit) for your desktop PC build
Before posting this article I shot a VLOG regarding the same and posted in my Youtube channel The Linux Channel. You can kindly watch the same:
Explore my lab's historical month wise power-usage trends: I started logging my entire lab monthly power-consumption readings. You can read the article HERE.
Off-Grid Solar Power System for Raspberry Pi: When you choose to use your Raspberry Pi device as your IoT based remote weather station or if you are
building Linux kernel (like kernel compilation) within the same, you need a good uninterrupted power source (UPS). But if you are using it on site or in some
research camping location you can choose to power your Raspberry Pi device with your custom off-grid solar power source. Kindly read my complete article about
the same HERE.

Suggested Topics:
Generic Home Lab Research
| 💎 TOFFEE-MOCHA new bootable ISO: | Download |
| 💎 TOFFEE Data-Center Big picture and Overview: | Download PDF |

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Featured Educational Video:

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Research :: Optimization of network data (WAN Optimization) at various levels:
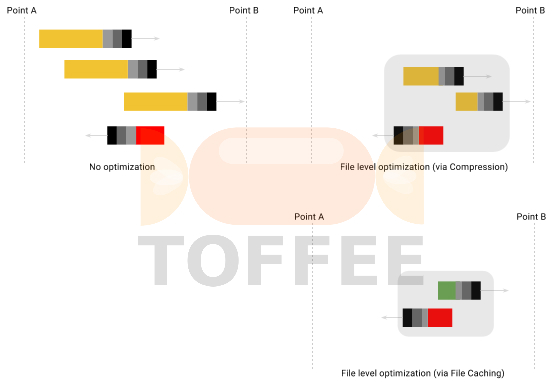
Learn Linux Systems Software and Kernel Programming:

Hardware Compression and Decompression Accelerator Cards:
![TOFFEE Architecture with Compression and Decompression Accelerator Card [CDN] TOFFEE Architecture with Compression and Decompression Accelerator Card [CDN]](http://sareesaremypassion.org/cdn/the-toffee-project/i/DOCUMENTATION/33/TOFFEE%20compression%20hardware.png)
TOFFEE-DataCenter on a Dell Server - Intel Xeon E5645 CPU: