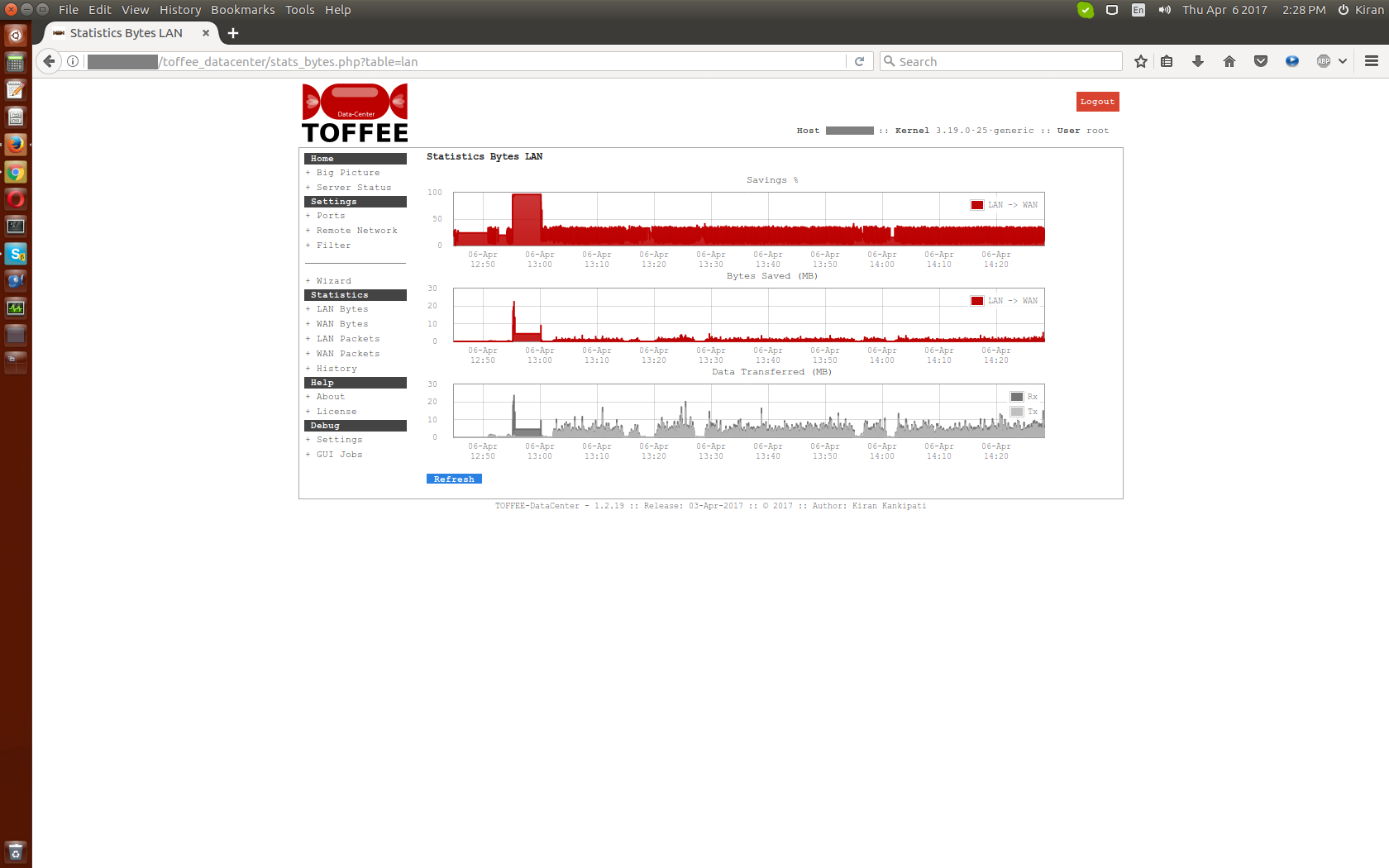
RESEARCH 》 A study on WAN Optimization Techniques
There are various techniques with which one can optimize their WAN Network Data. Any long distance communication can be considered as WAN Network. A decade ago any network connecting two countries, considered as a WAN network, and a network within a city as MAN and soon. But these days in general any long distance communication is considered as WAN Network. Such as your Mobile communication networks, Satellite networks, Space Networks (Deep space networks), Trans-Atlantic cable networks, etc.
You can optimize WAN links with techniques such as:
- File caching
- CDN
- WAN Optimization Devices:
- Commercial solutions: Riverbed, CISCO, etc
- or with open-source solution: TOFFEE
- QoS
- Compression
- Data De-duplication
Here is my Youtube video for more in depth coverage of this topic:
CDN Content Delivery Networks (a.k.a Content Distribution Networks): As the name says CDN technology allows you to share your content to large masses. CDN is a way you can scale up your website (or just about any content such as images, videos, live-concert streaming etc). You can build your own private CDN Networks or get can get CDN subscription commercial services via third-party CDN firms such as Akamai, Limelight, etc. I consider CDN as one among the WAN Optimization technologies, since it gives content owners/creators not only an option to distribute their content to masses across the world, but it also provides various benefits such as reliability, speed (faster page loads), etc.
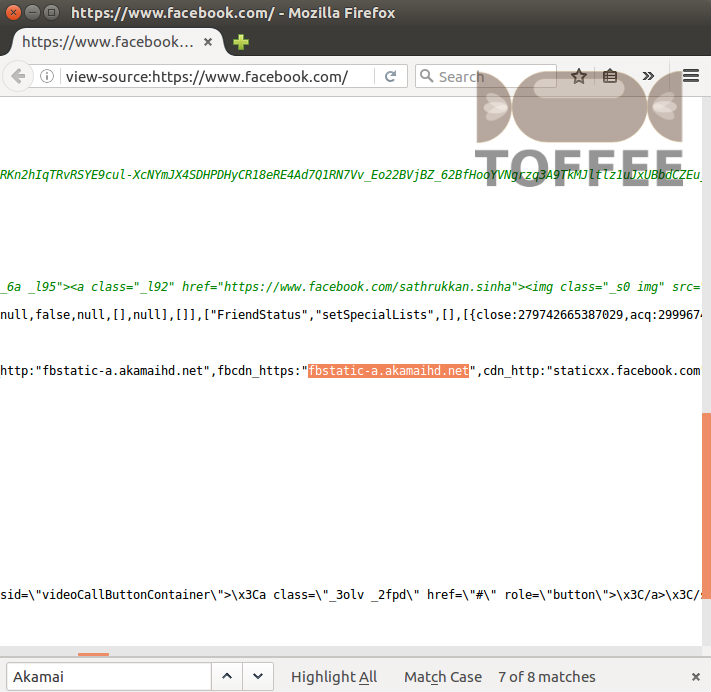
For example Facebook uses Akamai CDN. You can find the proof in the below screenshot of the facebook page view source code:
And in other case such as Google who built their own private super large CDN Network. In a case like Google they do not rely on third-party commercial CDN providers.
Instead they custom built from scratch their content distribution network according to their needs.
Here is my Youtube video for more in depth coverage of this topic:
Data De-duplication: Data de-duplication is a technique by which you can de-duplicate chunks of data (such as packet bytes and packets). De-duplication is a great way to eliminate redundant data. Unlike loss-less compression which is not so effective in all cases, de-duplication helps us save known types of data. Such as known protocols, patterns such as byte sequences with respect to protocol and so on.
For example, in TOFFEE I do packet-wise byte-wise data de-duplication which I call it as Packet Templating feature. It is called Templating since I created
thousands of templates for known frequently occurring traffic patterns specific to the packet's application protocol, packet's transport layer protocol
(such as TCP/UDP) and so on. It is the Packet templating feature in TOFFEE which is lot more effective saving bandwidth in VoIP sessions, HTTPS (SSL sessions),
remote desktop data (such as VNC, Teamviewer), remote MySQL Database connectivity, etc. Here is my Youtube video for more in depth coverage of this topic:
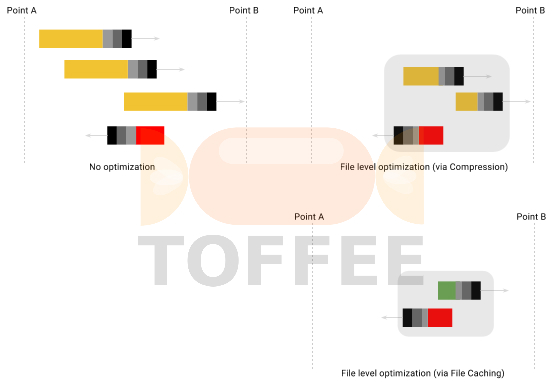
File Caching: File caching is the most oldest and fundamental WAN Optimization technology. One of the best example is caching feature in your browser which does not download pages or resources if they already exist in the browser file cache. And the other best example is your HTTP proxy file cache. Squid-cache is the most popular open-source file caching proxy for the Web supporting HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and more.
File caching technique reduces bandwidth and improves response times by caching and reusing frequently-requested cache-able web pages (and other file resources such as images, css, java scripts and soon). But unfortunately due to increase in use of dynamic SaaS web applications, file caching is no longer effective in optimizing modern dynamic websites such as Facebook, Youtube, Google-mail, your banking portals, etc. File caching is not applicable for dynamic data such as realtime VoIP, network data-base connections, streaming, Netflix, corporate back-end web-applications/portals and so on. Since the content shared and transferred is not in the form of individual files.
File caching is also useless if you access a file which is not so commonly accessed. The files stored in the cache for certain period of time, eventually it expire and they get purged. So it works purely on luck basis and the real world use-cases are getting limited day by day.
CDN is build with thousands of file-caching servers deployed world-wide. Or in other words CDN is a super-set technology which uses the file-caching technique
within its infrastructure. Lets assume you upload a Youtube video, once Google servers processes the same, the video is slowly distributed to various servers
(in various geographical datacenters) across the world. And any user residing close to any of these servers may get content from these servers. And if the file
does not exist in this server, it may pull the file from the main datacenter (or somewhere), and stores it in the file cache for future use. File caching
technique used in CDN is a well scripted predictable choreography. But file caching employed in a generic WAN optimization device is not that effective for the
same reasons discussed above. Here is my Youtube video for more in depth coverage of this topic:
Data Compression: Data compression specifically lossless compression is the most common WAN Optimization technique. Although data compression is not so effective for encrypted data (including VPN links), it is still highly effective in optimizing a majority of WAN Network data. If you have VPN links, try to install your WAN Optimization devices (such as TOFFEE), before the VPN devices. This way you can pass the optimized data into your VPN appliances. There are various losses compression algorithms exist and some of the popular ones are: LZ77, LZO, LZ4, LZ4-HC, etc.
TOFFEE supports LZ77, LZO and LZ4. LZO algorithm is enabled as a default kernel compile time option in any pre-compiled TOFFEE kernel binary releases (and OS firmware images) so far (till date 29-Jun-2016).
NASA have their own lossless compression variants and often they are customized. One of the well known algorithms which NASA uses is the LOCO-I (stands for Low Complexity Lossless Compression) which is mainly meant for compressing images. LOCO-I is a kind of lossless compression variant of JPEG. Which is why it is also can be sometimes called as JPEG-LS (stands for JPEG-Lossless). Based on LOCO-I NASA did hardware based solution which is FPGA-LOCO. Since it is hardware based, it is good in performance, reliability and extremely energy efficient.
Apart from this CCSDS have their own variant of RICE lossless compression algorithm.
Read article: A study on Deep Space Networks (DSN)
For more information on Deep Space Communication - Space Lossless compression refer my Youtube video below:
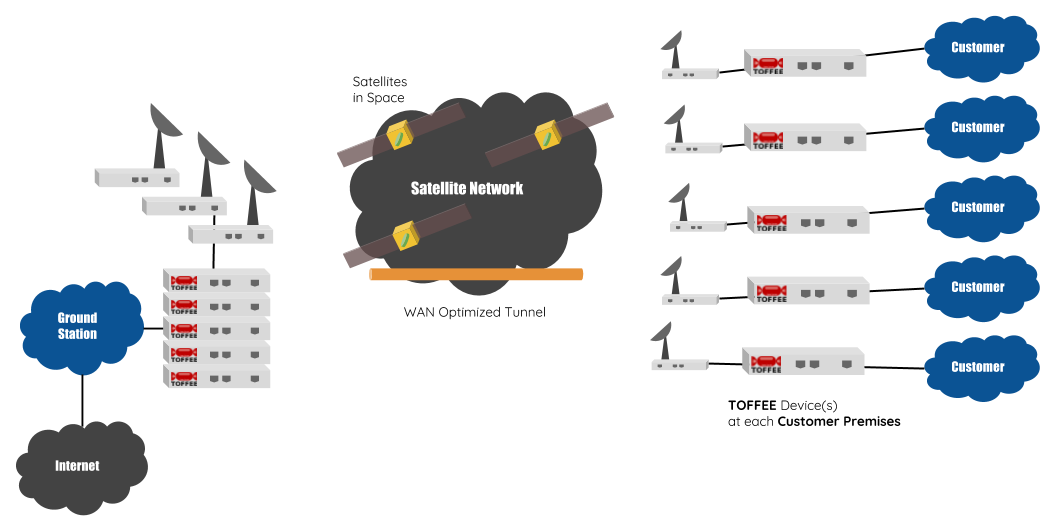
For example :: TOFFEE Optimized Satellite ISP Network:
Here is my Youtube video for more in depth coverage on this topic:
Suggested Topics:
WAN Optimization and Network Optimization
| 💎 TOFFEE-MOCHA new bootable ISO: | Download |
| 💎 TOFFEE Data-Center Big picture and Overview: | Download PDF |

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Featured Educational Video:
Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Research :: Optimization of network data (WAN Optimization) at various levels:
Learn Linux Systems Software and Kernel Programming:
![Linux, Kernel, Networking and Systems-Software online classes [CDN] Linux, Kernel, Networking and Systems-Software online classes [CDN]](http://sareesaremypassion.org/cdn/the-toffee-project/i/the_linux_channel_banner2.jpg)
Hardware Compression and Decompression Accelerator Cards:

TOFFEE-DataCenter on a Dell Server - Intel Xeon E5645 CPU: